The People Readiness Index, while valuable for internal HR considerations, can be even more powerful when viewed through the lens of direct business impact. By strategically focusing on these areas, organizations can unlock significant competitive advantages and drive sustainable growth.
What are the 6 Key Considerations For People Readiness?
1. Agility & Adaptability: Driving Innovation and Resilience
Ideas you can implement
- Scenario Planning & Simulation: Develop and run simulations based on potential future scenarios (e.g., economic downturns, technological disruptions, geopolitical shifts) to prepare the organization for unexpected challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- “Agile Sprints” for Business Units: Implement short-cycle “sprints” where cross-functional teams collaborate to rapidly test new products, services, or business models, fostering a culture of experimentation and rapid iteration.
- Dynamic Workforce Allocation: Create a flexible workforce model where employees can be quickly redeployed to address emerging needs or support high-priority projects, maximizing resource utilization and responsiveness.
Strategic Questions for the Leadership Team
- How can we build a culture that embraces change and thrives in uncertainty?
- What are the biggest threats and opportunities facing our business in the next 3-5 years, and how can we prepare our workforce to navigate them?
- How can we leverage technology to enhance our agility and responsiveness to market changes?
2. Future Skills: Driving Competitive Advantage
Ideas you can implement
- “Skills Marketplace”: Create an internal platform that connects employees with relevant learning resources, mentors, and project opportunities based on their skill gaps and the organization’s future skill needs.
- “Gig Economy” Partnerships: Collaborate with platforms that offer access to a pool of highly skilled independent contractors to augment internal capabilities and address short-term skill gaps.
- AI-Powered Skills Gap Analysis: Utilize AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze employee skills data, predict future skill requirements, and proactively identify and address potential skill gaps.
Strategic Questions for the Leadership Team
- What are the most in-demand skills in our industry and how can we ensure our workforce possesses them?
- How can we leverage technology to upskill and reskill our workforce at scale?
- How can we partner with educational institutions and industry leaders to develop the future skills we need?
3. Alignment: Driving Strategic Execution
Ideas you can implement
- “People Readiness Scorecards”: Develop scorecards that link individual and team performance to key business objectives, ensuring that employee contributions directly align with strategic priorities.
- “Talent Reviews” with Business Leaders: Conduct regular talent reviews with business leaders to discuss key talent priorities, identify high-potential individuals, and develop succession plans that support strategic goals.
- HR as a Strategic Business Partner: Embed HR professionals within business units to gain a deeper understanding of their challenges and opportunities, and proactively advise on talent strategies that support business objectives.
Strategic Questions for the Leadership Team
- How can we ensure that our talent strategy is fully aligned with the organization’s overall business strategy?
- How can we better communicate the link between HR initiatives and business outcomes to senior leadership?
- How can we empower HR professionals to become strategic business partners and contribute to the achievement of business goals?
4. Ambiguity Tolerance: Driving Innovation and Decision-Making
Ideas you can implement
- “Red Teams” & “Blue Teams”: Create “red teams” to challenge assumptions and identify potential risks, while “blue teams” defend existing strategies. This fosters critical thinking and improves decision-making in uncertain environments.
- “Fail Fast” Culture: Encourage experimentation and learning from failures. Celebrate “learning failures” as opportunities for growth and improvement.
- “Rapid Prototyping” & “Minimum Viable Products”: Encourage teams to develop and test prototypes and minimum viable products quickly and iteratively, allowing them to gather feedback and make adjustments before investing significant resources.
Strategic Questions for the Leadership Team
- How can we create a culture that embraces uncertainty and encourages experimentation?
- How can we equip employees with the tools and resources they need to make effective decisions in ambiguous situations?
- How can we reward and recognize employees for taking calculated risks and embracing new challenges?
5. Productivity: Driving Efficiency and Effectiveness
Ideas you can implement
- “Work-Life Integration” Initiatives: Implement flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options and flexible schedules, to improve employee well-being and enhance productivity.
- “Focus Time” & “No-Meeting Days”: Encourage uninterrupted periods of focused work by designating specific times for deep work and minimizing unnecessary meetings.
- “Automation & AI-Powered Tools”: Leverage automation and AI-powered tools to streamline administrative tasks, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
Strategic Questions for the Leadership Team
- How can we create a work environment that maximizes employee productivity and engagement?
- What are the biggest productivity bottlenecks within our organization, and how can we eliminate them?
- How can we leverage technology to improve employee productivity and efficiency?
6. Career & Succession Planning: Driving Long-Term Sustainability
Ideas you can implement
- “Internal Mobility Platforms”: Create internal platforms that allow employees to explore career paths, identify development opportunities, and apply for internal job openings.
- “Mentorship & Coaching Programs”: Establish robust mentorship and coaching programs to develop high-potential employees and prepare them for leadership roles.
- “Reverse Mentoring”: Encourage cross-generational mentoring where junior employees mentor senior leaders on emerging technologies and trends.
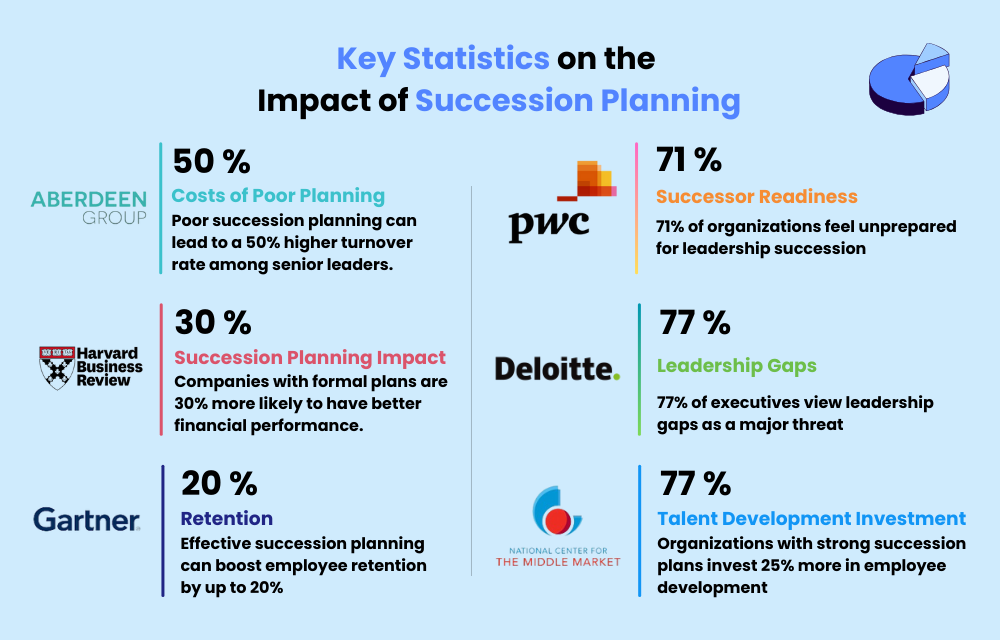
Strategic Questions for the Leadership Team
- How can we ensure that we have a deep bench of talent to succeed current leaders?
- How can we create a culture of internal mobility and career growth within the organization?
- How can we effectively identify and develop high-potential leaders?
By focusing on these areas and asking the strategic questions posed, organizations can transform the People Readiness Index from an internal HR metric into a powerful driver of business impact. By cultivating a highly skilled, adaptable, and engaged workforce, organizations can unlock innovation, improve decision-making, enhance productivity, and ultimately achieve sustainable competitive advantage in today’s dynamic and challenging business environment.

Abhijit Bhaduri is a celebrated thought leader and LinkedIn Top Voice with over a million followers. With leadership roles at Microsoft, Wipro, and global giants like PepsiCo and Tata Steel, he brings deep expertise in Learning & Development. The acclaimed author of Don’t Hire the Best and Dreamers and Unicorns, Abhijit has also shared insights on platforms like Forbes and hosted the popular podcast series Dreamers and Unicorns.